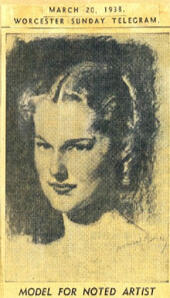HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
Places Where Women Made History
Reflecting a decorative and eclectic blend of Italian Renaissance, Gothic and Islamic influences, the 23-story Barbizon Hotel represents one of the earliest residential alternatives for women moving to New York City to take advantage of the new professional opportunities of the 1920s. Young women began leaving the traditional family home in search of career opportunities brought on by the era's economic expansion. The Barbizon provided a refuge for many of these women, and its owners sought to create an environment that reinforced the values of the families from which the women had come. Codes of Conduct and Dress were enforced, no men were allowed above the lobby floor, and prospective tenants needed three letters of recommendation to be considered. Despite these apparent constraints, the Barbizon later hosted many social, intellectual and athletic activities and, and in recent years attracted a variety of famous tenants, including entertainers Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen and Liza Minnelli. The Barbizon was also active in promoting women's organizations, providing meeting space to groups such as the National Junior League, the Arts Council of New York, and the Wellesley College Club. Today, the Barbizon operates as a standard hotel.
HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
Places Where Women Made History
Reflecting a decorative and eclectic blend of Italian Renaissance, Gothic and Islamic influences, the 23-story Barbizon Hotel represents one of the earliest residential alternatives for women moving to New York City to take advantage of the new professional opportunities of the 1920s. Young women began leaving the traditional family home in search of career opportunities brought on by the era's economic expansion. The Barbizon provided a refuge for many of these women, and its owners sought to create an environment that reinforced the values of the families from which the women had come. Codes of Conduct and Dress were enforced, no men were allowed above the lobby floor, and prospective tenants needed three letters of recommendation to be considered. Despite these apparent constraints, the Barbizon later hosted many social, intellectual and athletic activities and, and in recent years attracted a variety of famous tenants, including entertainers Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen and Liza Minnelli. The Barbizon was also active in promoting women's organizations, providing meeting space to groups such as the National Junior League, the Arts Council of New York, and the Wellesley College Club. Today, the Barbizon operates as a standard hotel.
HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
For a small-town girl with a dream, from the Roaring 20s through the 1960s, there was no address more glamorous than New York’s "women only” Barbizon Hotel. A combined charm school and dormitory, it would shelter a parade of yet-to-be-discovered damsels—Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more—nurture their ambitions, and leave some with broken hearts. The author delves into the Barbizon’s mystique, as well as the darker side of its Stork Club–and–stardust allure.She sat by the window, watching the world rumble by as the train barreled toward New York City. In her purse was $60 from her father, a man of stiff Iowa breeding who worked at the family lumber company back in Des Moines. The money was intended to buy three days in Manhattan, three days that would begin shortly after her arrival at Grand Central, where she would gently disembark in her chartreuse-and-black dress with its tightly fitted houndstooth jacket, accented by a jaunty black sailor hat.Cloris Leachman was 20 years old in 1946, and like thousands of girls before and after her, she had come to New York to find something far bigger than a holiday. She had backed into the Miss America Pageant as Miss Chicago, at one point spending hours practicing how to walk in figure eights to impress the judges. She didn’t win, but it didn’t matter, because what she was looking for couldn’t be found amid the honky-tonk of the Atlantic City Boardwalk. What she was looking for was stardom.On a chilly December day three months later—25 years before she would float onto the stage at the Oscars (winning best supporting actress for The Last Picture Show) and declare, "I’m having an amazing life, and it isn’t over yet”—Cloris Leachman swept through the tony aisles of Bergdorf Goodman in a full-length beaver coat that covered a tailored green wool suit, with matching suede heels. Stepping out onto the sidewalk in front of the Christmas windows of the department store, she looked over at the twinkling lights of the Plaza hotel, smiled, and sighed. She was an understudy in two different Broadway plays. She was dating a worldly, handsome man. And, best of all, she was living at the most glamorous address a girl could have if she dreamed of becoming a star: the Barbizon Hotel for Women, at the corner of Lexington Avenue and 63rd Street.Standing there in the night air, with Manhattan laid out like a magic carpet in front of her, was, 83-year-old Leachman says today, "the most exciting moment of my life.”There were other "women only” hotels in town: the Martha Washington had opened in 1903 (gaining notoriety in the 1960s when actress Veronica Lake, divorced and broke, was discovered working as a barmaid); the Trowmart Inn began taking residents in 1910; the Parkside Evangeline was a staple of Gramercy Park. But the Barbizon was the city’s elite dollhouse. Built by Murgatroyd and Ogden, the 23-story building had an exterior of pinkish-coral brick accented with ocher sandstone in the Romanesque, Gothic, and Moorish styles, with an obelisk design that gave its façade the appearance of one of the Houses of Parliament jutting into the Manhattan sky.It opened in 1927, hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern Millies pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor. From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school and dormitory, one where fretting parents could be confident their girls would be kept safe—and chaste. No men were allowed above the lobby without strict supervision, and parents could require their resident daughters to sign in and out at the front desk. Some were even given their own chaperones. Girls who came in late or, in the parlance of one staff matron, "in bad shape” were spoken to. According to a writer for Time magazine, it was "one of the few places in Gomorrah-on-the-Hudson where a girl could take her virtue to bed and rest assured it would still be there next morning.” What’s more, the building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood.”The hotel’s reputation for housing lovelies really bloomed in the mid-1940s—around the time Cloris Leachman walked through the doors—when it acquired the haute mystique that became its stock-in-trade. It was relentlessly marketed and written about in gossip columns and in the back of fashion magazines, feeding the fantasies of girls who dreamed about becoming, in the words of a breathless advertisement, one of the "ambitious, discriminating young women” who became "Barbizon girls.” The Barbizon sold not a residence but, rather, an ideal: life as portrayed in the pages of Photoplay. "They would feed little snippets and bits and pieces to the columns around town, so that the Barbizon began, in and around the years around World War II, to become known for attracting a certain kind of young lady,” says Betsy Israel, the author of Bachelor Girl, a social history of single women in New York in the 20th century. "That’s how it promoted itself.”In the hotel’s fizzy heyday, from the 40s through the late 60s, it housed a roster of remarkable women in their not-yet-discovered years. Joan Crawford, Gene Tierney, Barbara Bel Geddes, Peggy Cass, Dorothy McGuire, Grace Kelly, Elaine Stritch, Liza Minnelli, Ali MacGraw, Cybill Shepherd, and Candice Bergen all stayed, as did future writers Eudora Welty, Joan Didion, Ann Beattie, Mona Simpson—and Sylvia Plath, who set part of The Bell Jar at a fictional Barbizon. Literary agent Annie Laurie Williams, who would later represent both John Steinbeck and Margaret Mitchell, was a resident, along with fashion designer Betsey Johnson and columnist and presidential speechwriter Peggy Noonan. Molly Brown, the renowned and "unsinkable” survivor of the Titanic, who would later be immortalized in her own Broadway musical, died there in 1932. Edith Bouvier Beale, the cousin of Jacqueline Kennedy who became a cult figure as "Little Edie” in Grey Gardens, checked in for five years, starting in 1947.Determined to keep a watchful eye over her show ponies (and to keep them out of the tabloids), Eileen Ford began renting rooms there shortly after founding her famed modeling agency with her husband, Jerry, in 1946. Some of Vogue’s most fetching cover models lived inside, including Jean Patchett, Gloria Barnes, and Dolores Hawkins, who once had a 1957 Ford Thunderbird delivered to the front door. "Where else could you put girls who were only girls?” recalls Ford, still exacting and vinegary at 88. "It was safe, it was a good location, and they couldn’t get out.”The thick coat of stardust only burnished the Barbizon’s reputation as a playgirl mecca, one reinforced by cabdrivers, who regularly tried to bribe Oscar, the hotel’s portly doorman, for fares. The Katharine Gibbs Secretarial School also stashed its protégées inside, shoulder-padded young women straight from the pages of Kitty Foyle. (In the opening of the 1940 film adaptation, a gaggle of date-seeking gals step off an elevator as one asks aloud, "After all, what’s the difference between men bachelors and girl bachelors?,” prompting Ginger Rogers’s Kitty to acerbically retort, "Men bachelors are that way on purpose.”)For fretting mothers, comfort came in the Barbizon’s aura as a particularly genteel fortress run by an army of skulking Mrs. Danverses, who glided through the halls and guarded the elevators, issuing tart remonstrations to those who dared to breach policies on cooking (not in the rooms), dress (neat and presentable), and men (none). "You were a lady there,” says former Charlie’s Angel Jaclyn Smith, who as a teenager in 1965 arrived at the Barbizon from Texas to study ballet. Inside she befriended model Dayle Haddon, who would become the face of L’Oréal, and Margo Sappington, later a dancer with the Joffrey Ballet and choreographer of the infamous nude musical Oh! Calcutta! "This was another time and place,” Smith insists. "I really dressed up: hose, heels. I don’t know how I walked. I looked like I was going to church every day.”While its 700 rooms were spartan (electrical appliances were banned) and impossibly tiny, the hotel sold itself in glossy brochures as the gold standard in single-girl living, "a cultural and social oasis” that offered a swimming pool, a library, recital rooms, a sundeck, a solarium, squash and badminton courts, and a formal dining room imbued with "Old Charleston atmosphere.” A social director issued a weekly "Court Circular” listing sundry activities, from organ recitals to Shakespeare readings. Afternoon tea was a must, its petite finger sandwiches serving as the day’s meal for many girls whose families were not so grand in their allowances. There were nightly bridge games and competitive backgammon tournaments and various lounges where women were allowed to entertain gentlemen callers—supervised, naturally.The hotel had the feel of a particularly luxe convent, which was hardly accidental. The expansive lobby, accented by potted ferns, Oriental carpets, and antique English lanterns, contained a sweeping staircase that led to the mezzanine, from which girls could peer down over latticed-wood railings to evaluate prospective dates below.Predictably, the Barbizon attracted a fair number of men seeking to woo its denizens. In the late 1940s, J. D. Salinger picked up Barbizon girls at the hotel’s adjoining drugstore, whisking them down to modish Greenwich Village and enchanting them with wild stories; one left believing that he was a goalie for the Montreal Canadiens. In the 50s, Manhattan millionaire Edgar Ausnit would routinely send a car around to the Barbizon to retrieve a few fawns and bring them back for impromptu parties in his Fifth Avenue penthouse, where he would entertain pals such as Cary Grant.Only the most brash suitors were able to break the rule that forbade male access above the first floor or outside of approved lounges (pass required), though tales of the creative lovelorn quickly became legend. Men crammed into dumbwaiters or passed themselves off as fathers, doctors, priests. Carmen Dell’Orefice, one of Ford’s most ravishing models in the 1950s, says that during that time many uptown girls were patients of John MacGuigan’s, the dashing Upper East Side gynecologist who would later marry DuPont heiress Lisa Dean Chandor. Many young men—some successfully, others not so much—used MacGuigan’s name to try to wangle their way upstairs.But not Malachy McCourt. In 1958 the Irish storyteller, then 26, had opened a saloon at 63rd and Third called Malachy’s ("the best hamburger in America”). In his thick brogue, he’d welcome the wide-eyed Barbizon girls, who would drift in to take a seat at his bar, a rare courtesy to women of that era. "On occasion I would escort them back to the hotel,” he remembers. "They were usually girls from the Midwest, innocent as a rule, but lovely-looking young things.” On cue, the girls would distract the matrons at the front desk as McCourt scurried up the back stairs, en route to "a rather swift and fumbly-tumble kind of thing.” Afterward he’d brazenly walk out through the front door, tipping his hat to the desk ladies as he left.Not all girls were so bold. "If anybody could’ve, I would’ve,” says Cybill Shepherd, who at 18 came to the Barbizon from Memphis, in 1968, after winning a national modeling competition. "That’s my speciality—sneaking ’em in, sneaking ’em out. But I wouldn’t have dared to do that there. It was an institution.” If the Barbizon had a face, it was that of Grace Kelly. After High Noon and Alfred Hitchcock made her a star, in the early 50s, Kelly and her prior residency were relentlessly hyped in hotel ads intended to brighten the Barbizon’s sparkle—because she represented not what the Barbizon was, but what it aspired to be. The Barbizon wanted its poster girl to be Lisa Fremont, Jimmy Stewart’s sophisticated girlfriend in Rear Window, who had all of Kitty Foyle’s snap and guile, but was also swathed in filmy negligées, A-line dresses, opera gloves, and smart pillbox hats with netting.Kelly’s domineering father, in Philadelphia, had allowed her to enroll at the American Academy of Dramatic Arts in 1947 on the condition that she live at the Barbizon, thinking it would ensure discipline. Fat chance. Kelly would soon make waves by performing exotic dances in the hallways, while scantily attired, and for her facility in arranging covert romantic assignations in the darker corners of the hotel lounges. It all left her floormates agog, envious—and admiring. "I think a lot of the reason Grace became so famous for having lived there was because she never really changed,” says Philadelphia friend Maree Rambo, who often visited Kelly at the Barbizon and was later a bridesmaid in her fairy-tale wedding, in Monaco, in 1956. "She had a tremendous sense of humor.”The gauzy flair conjured by her public image enhanced the Barbizon’s as the hotel itself grew into a character, its ethos reflected in films as diverse as Stage Door (the soapy 1937 tale of a group of aspiring actresses, played by Katharine Hepburn, Ginger Rogers, and Lucille Ball) and the 1959 classic The Best of Everything—with Hope Lange as the archetypal Barbizon girl. The hotel would turn up in a dozen best-sellers: in facsimile form in Mary McCarthy’s 1963 novel, The Group, and in potboilers by Jacqueline Susann, Jackie Collins, and Judith Krantz (whose Scruples heroine, Billy Ikehorn, was threatened with residing at the Barbizon as punishment), as well as Herman Wouk’s The Winds of War and John Updike’s In the Beauty of the Lilies. The Barbizon mystique had its underside too, as reflected in Gene Kelly’s harsh words to a love-struck Natalie Wood in Marjorie Morningstar, in 1958. In the film, Kelly memorably barks that he has no time for "another Shirley”—his nickname "for the respectable middle-class girls who like to play at being worldly.”Grace Kelly may have been its public face, but the Shirleys would prove to be the Barbizon’s lifeblood. "When I got the letter of acceptance, you would have thought I had been accepted to Yale or Harvard,” remembers Barbara Cloud, a former columnist for the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, who in 1951 made her way from Uniontown, Pennsylvania, to become an actress. "We were all from Okefenokee,” adds Betsey Johnson, who arrived from Wethersfield, Connecticut, in 1964. "I can’t remember too many big-city girls.”Indeed, much of the Barbizon clientele, though well groomed, well behaved, and well dressed, consisted of girls from Fresno and St. Louis and Omaha playacting at sophistication. Bachelor Girl author Israel says the typical young woman arrived with her suitably chic wardrobe from a better local department store, went on dates in formalwear, and "received roses in very long boxes with mysterious cards.” While not of the social strata of the Ford models or Broadway starlets, these girls nonetheless discovered that the Barbizon was a play for which they had very good seats. They spent their days taking classes or looking for jobs, dashing home to squeal about sightings of Robert Goulet at B. Altman or Peter Sellers filming down the street. "Kitty Carlisle lived in the same block, so if we were walking toward Third Avenue we would sometimes see her at night waiting for her driver, and she would be in this wonderful long gown and jewels,” says MaryAnne Powers, a medical clinician who arrived from Oak Park, Illinois, in 1963, to study fashion merchandising.
This "small-town girl comes to the big city” vibe was never more apparent than with Mademoiselle’s "guest editors.” Each August, the fashion magazine published its College Issue, and every June, 20 contest winners would breathlessly arrive at the doors of the Barbizon for a month-long stay and a date with publishing glamour. Over the years, Betsey Johnson, Ali MacGraw, and writer Francine du Plessix Gray, stepdaughter of Condé Nast editorial director Alexander Liberman, were among the "Mlle.” (pronounced "Millie”) editors-in-training, who rode a dazzling carousel of movie premieres, society luncheons, fashion shows, and photo shoots. "You got to go to Helena Rubinstein’s cocktail party and see her jewels and her art collection,” recalls the writer Gael Greene, a Mademoiselle guest editor along with Joan Didion in 1955. "There were many perks, many glamorous stops for somebody from the Middle West, like me.”The coeds, often with names like Mopsy and Tizzie and Mimi, would produce stories with titles such as "Anything as Long as It’s Paisley” and "Where There’s a Man, Wear Red,” then they would spoon vichyssoise at the Drake, tour Cartier and The New York Times, and get interviewed by syndicated gossip columnist Earl Wilson. The college editors of 1964 were even whisked away to London, where they were guests at a party inside Fleur Cowles’s Piccadilly apartment. "It was a totally different world. The Upper East Side back then was just full of Middle-European restaurants and interesting people,” Greene says. "I fell in love every other day.”In her roman à clef, The Bell Jar, Plath—a Mademoiselle guest editor in June 1953—captures the experience vividly, including her own last night in New York, when she allegedly threw her entire wardrobe off the roof of the Barbizon. In keeping with the dolorous tone of the novel, however, that pivotal month is viewed through a lens, darkly. Her most interesting insight into the minds of the Barbizon girls comes in a passage where Plath’s alter ego, Esther Greenwood, daydreams during a magazine-sponsored field trip to the U.N., viewing her life as a fig tree with its different branches denoting different choices: wife and mother, poet, sensual adventuress, and so on. "I saw myself sitting in the crotch of this fig tree, starving to death, just because I couldn’t make up my mind which of the figs I would choose,” Esther muses. "I wanted each and every one of them, but choosing one meant losing all the rest, and, as I sat there, unable to decide, the figs began to wrinkle and go black, and, one by one, they plopped to the ground at my feet.”"I remember sitting up in my little pink room—my room was Pepto-Bismol pink—and looking down Lexington and having a little blue notebook to write in, and feeling like I had never been so lonely in my life,” says Cybill Shepherd. "And wondering how I would ever make it in this vast city just stockpiled with brilliant people.”Such internal struggle, such yearning—for the right job, the right guy, the right life—was a constant companion to many of the girls who lived within the Barbizon’s cloistered walls. This was never more apparent than in the hotel’s famous coffee shop, the crossroads where the girls who were going to make it crossed paths with those who were not. The place was noisy and bustling—one girl rushing out to a go-see, another sliding into the booth to replace her and telling dejected tales of doors slammed in her face.Shelley Hack was 15 in 1962 when she was discovered sailing off Greenwich, Connecticut, and was immediately signed to Ford. A whirlwind two weeks later, Ford put her up—alone—for the night at the Barbizon before one of her first bookings. Feeling all grown up, Hack excitedly slipped into a booth in the coffee shop to have dinner. There she met a five-foot-two-inch aspiring model from Florida who had just won a beauty contest; her small town had chipped in to send her to New York to make her dreams of modeling fame come true."I looked around the room, and all of a sudden the whole thing came into focus,” says Hack, who would go on to become famous as the face of Revlon’s Charlie perfume, and later as Tiffany Welles, the Brahmin member of Charlie’s Angels. "The room was full of girls who had done everything I hadn’t had to do. They were far from home. They didn’t have family backup. They didn’t have money. They wanted something. I had it, and I didn’t even want it. I respected it, I knew it was an opportunity, but it wasn’t something I had dreamed of, planned for, babysat and saved money for. I wasn’t invested in it.”For many of the girls who were, life at the Barbizon came with an expiration date. "I didn’t have the temperament to pursue a career in the theater,” says columnist Barbara Cloud, who lasted six months in Manhattan back in 1951. "I realized that soon after I got there. If someone looked at me sideways I was a nervous wreck. I was just not equipped to handle all of that.”Then the gloves came off.Gael Greene, who had been a Barbizon girl two years earlier, was working for the New York Post in 1957 and returned to the hotel only to grab it by the choker. In a withering series of articles published under the rubric "Lone Women,” Greene documented—in often painstaking, wince-inducing detail—the empty, haunted lives of the lodgers who were not Gene Tierney or Grace Kelly. In place of the screen-siren images, Greene focused on the vacant, naïve midwestern girls, jaded lounge singers whose big break had never come, and cranky old fussbudgets bickering in the hallways. "In those days, many young women and their parents were just riveted on the dangers and risks on every street corner in New York,” Greene says now. "For me, it was a revelation of so many paralyzed, petrified, enterprising young women.”The Barbizon girls, Greene wrote, were "seeking something indefinable—something to do, a rent-paying job, romance, the alchemy that will transform an ordinary girl into an extraordinary woman.” In other words, to fulfill the promise of the brochure ads. But Greene saw young women (and several of their bitter, elderly counterparts) who were waiting for life to happen, rather than making it happen themselves. The series was a Sherman’s March of lonely girls in phone booths crying to their mothers, of mail and phone messages that never came, of the heartbroken in pin curls, sitting slack-jawed in the communal TV room shoveling in ice cream from cartons. Greene had exposed one of the Barbizon’s most dreadful secrets: that for every girl holding on to her hat and click-clacking through the lobby on her way to a date at the Stork Club, there was another left behind, wearing a flannel nightgown and a face smeared with cold cream, waiting for Milton Berle to come on. (On occasion in the 1960s, African-American women boarded there, but from its earliest days the residence was assertively white-bread.)Plath hints at this darker side of the Barbizon in The Bell Jar, though there were even more tragic cases—the ones who, like Kay Hamilton’s struggling actress in Stage Door, climbed to the top of the hotel, stepped out onto the terra-cotta terrace, and flung themselves to their deaths. (A similar fate befalls Kay Peterson in The Group.) The Barbizon suicides had all the gothic tragedy of the Brontës, and proved irresistible fodder for New York’s tabloids. "I can’t say I personally felt rattled by it,” notes Alice Delman, who moved to the Barbizon in 1959 and today evokes the image of Margaret Thatcher. She serves as a sort of unofficial spokeswoman for the 11 "ladies” (as staff members quietly refer to them), veterans from the glory days who still live in the building. "Some [of the suicides] might have been hushed up, too—it’s not good publicity for a hotel.”Nothing, however, could have been as damaging as the sense of foreboding that washed over a girl when she passed one of the Women—the code name for the residents who had come and never left. While some, like Delman, were vibrant, professional types, a good number were secretive and dour, taking corner tables in the coffee shop and dining alone in their dowdy skirts, sensible shoes, and black nylons, looking at many a passing girl with a mixture of scorn and suspicion. "I remember thinking that they must be lonely,” Powers says, "because they would be out talking at night from room to room. They wouldn’t go into each other’s rooms, but they’d be in long conversations leaning against their open doors. It was a safe, glamorous place for us, but we wondered why they were there.” No girl wanted to be branded with the "S” label—Spinster. "If you were living there when you were over 25, it was over,” says author Israel. "The rest of the world worried about becoming a bag lady,” recalls Joyce Schwarz, a writer in Marina del Rey, California. "We worried about becoming a Barbizon lady.”By the end of the 1960s the chic Barbizon of legend was more or less dead, its pencil-skirt-and-pearls sensibility replaced by the British invasion of mad-mod Twiggy and sleek Emma Peel, the era’s new swinging singles. Grace Kelly inevitably gave way to Grace Slick. Other buildings opened to cater to the city’s burgeoning stewardess clientele, and lacked the intrusive busybodyness of the Barbizon. And the outré girls who had pioneered single life in Greenwich Village, once painted as oddities and bohemians, had by the late 60s paved the way for the single-minded career women who would eventually rally around the crusade for women’s equality in the 1970s. No one was doing afternoon tea and organ recitals anymore.The hotel was bought and sold several times, briefly passing through the hands of the Zeckendorfs and hotelier Ian Schrager. Now owned by a Philadelphia development group, the Barbizon was eventually converted into a bona fide hotel and renamed the Melrose, then closed in 2005 for a complete gut job and flipped into a luxury condominium building, with 69 units priced from $1 million up to $17 million for a penthouse. Re-christened Barbizon63, the building has an interesting cross section of owners (François Pinault, the French billionaire and father-in-law of actress Salma Hayek; British actor-comedian Ricky Gervais), many of whom have purchased properties as pieds-à-terre. The Women from the "old” Barbizon remain, grandfathered by New York rent laws. "They tend to keep to themselves,” says Tony Monaco, Barbizon63’s general manager.But the Barbizon of yore is not completely dead. Julia Stiles has optioned The Bell Jar for a film, and the Style section of the Times recently ran a breezy story on the comeback of women’s hotels in New York, populated by young upstarts seeking much of what their Barbizon forebears did: camaraderie, safety, light mothering, and a place to launch their lives."The Barbizon had an aura of maturity, of responsibility, of adulthood,” says Judith Sherven, a psychologist and an author who arrived at the hotel in 1966 as an aspiring 21-year-old actress, soon landing bit parts on Star Trek and I Dream of Jeannie. "You were expected to behave.”Which was the point, after all: to develop girls into young women. Some went on to fame; most did not. But for all who swept in and out of the Barbizon, there was a feeling—a very deep, very meaningful feeling—that they had been part of a special sorority, that they had gotten to experience, if only for several days or a week or a month, a charmed life that few girls ever did. "We used to save their money for them, to pay their income tax,” Eileen Ford says of her Barbizon girls. "One girl spent $500 we had set aside to pay hers—for a Dior. That’s how they were when they weren’t working. They wore gloves, hats with veils, had cigarette holders. They believed that world, they really did.”At the end of Kitty Foyle, Ginger Rogers’s title character—having ditched the devilish rake for the stable doctor who wants to marry her—leaves the "Pocahontas Hotel for Women” and climbs into a cab. The chipper doorman asks if she’ll be away long. "Permanently,” Kitty replies with a smirk, then turns her eyes forward as the cab pulls her away to the rest of her life.Vanity Fair, April 2010
1932 – VOGUE prints its first full-color photographic cover
1938 - Early Barbizon model headshot
1939 - GLAMOUR Magazine launched
1939 – St. Clair McKelway Recommends Phyllis McCarthy to Barbizon
September 28, 1939Bruno R. Wiedermann,
The Barbizon,
Lexington Avenue and 63rd street,
New York City.Dear Mr. Wiedermann:I have your letter of September 26 telling me that Miss Phyllis McCarthy of Worcester, Massachusetts, has given you my name as a reference and asking me if I would give you "my opinion as to the desirability of Miss McCarthy, which would of course be held in strict confidence.” It certainly is a coincidence that you should write me just at this time, when the desirability of Miss McCarthy is practically the only thing on my mind. I’ve been telling everybody I know how desirable she is and haven’t even asked them to keep it in confidence, since, as far as I’m concerned, my opinion of Miss McCarthy can be put in electric lights over Broadway or written in the sky. I never thought I would be confiding in a hotel manager about her but you asked for it, Bruno, so here goes: Miss McCarthy is just about as desirable as a girl can be. She is tall, just about the right height for a six-foot man, blond, with longish hair that has a way of falling all around her face in spite of the efforts of hair dressers and herself to keep it orderly. It is nicer when not orderly.Her features have a lot of character and they all stand out clearly and boldly. There is nothing sneaking or understated about her nose, mouth, eyes or ears. They are all fair-sized and forthright. They have a symmetry, of course, which sometimes fools an observer like myself into thinking that she is a small girl with a tiny face; this is just an illusion and you can put it down to my dreamy state of spirit when it is placed alongside Miss McCarthy’s desirability. Miss McCarthy is no pretty baby; she is strong and healthy and probably could lick an average male office worker hands down in a free-for-all, catch-as-catch-can-battle. To keep herself in this condition, which is used mostly as a reserve defence, like the German West Wall, she rides on occasion, handles the jibs and sometimes the helm of a sloop, dances until four and fights her way in and out of the Stork Club, using her escort as a club. She pretends sometimes to be demure and feminine, which she no doubt is when she wants to be, but a man would be a fool to rush those fortifications of hers without first battering them down with flowers, hamburgers, exotic fruit, steak, symphonic music, French pastry, and honeyed words. Even then he is taking his life in his hands; but in spite of that he would be a bigger fool if he didn’t run the risk.I could go on like this for the length of a book. What else do you want to know? She has a cheerful disposition on the whole and laughs a lot, but not in a silly fashion. She dresses beautifully and is inclined to buy a grey suit for $150 or so when she hasn’t got $150, much less a so; she is apt, also, to choose a grey suit because she happens to like that particular grey suit and entirely disregard the fact, in doing so, that she has neither grey shoes, grey hat or grey gloves and consequently will be forced to buy these, too, with what she has left out of the $150 or so she didn’t have in the first place. The charming thing about all this is that she will look wonderful and more desirable than ever in the grey suit, grey gloves, grey hat, etc., and that, if she gets more desirable than she is now she will drive me nuts — and you, too, Bruno, if you get to know her even casually, old fellow.But why should I be telling you all this anyway? If I find you, or anybody else at your hotel, using this information for anything other than to try to bring Miss McCarthy into that congenial group of young women you speak of in your letter, I will tie lead weights on your ears, Bruno old fellow, and drop you into the cold pool in the Turkish bath at the Biltmore. Remember that. And remember, too, that if you want to tell what I think of Miss McCarthy to the world, you have my permission to do so. I would suggest a suitable neon sign about twenty feet high, say, and thirty feet long, extending from the extreme south side of your building around the corner to the extreme east side, with the words, "Miss McCarthy Is the Most Desirable Girl in New York – St.Clair McKelway, the New Yorker.” Or, "Is Miss McCarthy Desirable? Boy! Says McKelway.”If I can be of any further service to you just call on me.Sincerely yours, St. Clair McKelway
HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
1944 – Fashion labels and designers Harveys, Henry Rosenfeld, January, Jaunty Junior, Junior Guild Original, Mendoza, Trigger Cloth, Vera Maxwell
HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
The World Famous Garment District
New York City is arguably the fashion capital of the United States and the entire world because the industry based there generates over $14 billion in annual sales and sets design trends which are mirrored worldwide. The core of the industry is Manhattan's Garment District, where the majority of the city's major fashion labels operate showrooms and execute the fashion process from design and production to wholesaling. No other city has a comparable concentration of fashion businesses and talent in a single district.
The Garment District is home to a number of well-known designers, their production facilities, warehouses, showrooms, and suppliers of fabric and materials. Many in the industry looked to Barbizon to book models over the decades and allege that this dense concentration of talent, entrepreneurship and supply stores functions like an ecosystem in which each of the parts help sustain the whole. Major fashion labels such as Carolina Herrera, Oscar de la Renta, Calvin Klein, Donna Karan, Liz Claiborne, Nicole Miller, and Andrew Marc have showrooms, production facilities, or support offices located in the Garment District.
Nineteenth Century Tailor Made
Prior to the mid-nineteenth century, the majority of Americans either made their own clothing, or if they were wealthy, purchased "tailor-made" customized clothing. By the 1820s, however, an increasing number of ready-made garments of a higher quality were being produced for a broader market.The production of ready-made clothing, which continued to grow, completed its transformation to an "industrialized" profession with the invention of the sewing machine in the 1850s.The need for thousands of ready-made soldiers' uniforms during the American Civil War helped the garment industry to expand further. By the end of the 1860s, Americans bought most of their clothing rather than making it themselves.German and Central European immigrants to America around the mid-19th century arrived on the scene with relevant business experience and skills just as garment production was passing from a proto-industrial phase to a more advanced stage of manufacture. In the early twentieth-century a largely Eastern European immigrant workforce powered the garment trades. With an ample supply of cheap labor and a well-established distribution network, New York was prepared to meet the demand. During the 1870s the value of garments produced in New York increased sixfold. By 1880 New York produced more garments than its four closest urban competitors combined, and in 1900 the value and output of the clothing trade was three times that of the city's second largest industry, sugar refining. New York's function as America's culture and fashion center also helped the garment industry by providing constantly changing styles and new demand; in 1910, 70% of the nation's women's clothing and 40% of the men's was produced in the City.
HISTORY
About Barbizon New York City
Notably the first and original fashion modeling agency in the world, Barbizon Agency was founded in 1939 on Fifth Avenue in New York City. For over 75 years, since its' opening in 1939 by fashion model Helen Fraser, Barbizon has been in the forefront of the industry, and a leader in developing the careers of Women, Men, Kids and Teens all over the world.
History
The Era of Barbizon - "The Girl with a Job"On Election Day in 1920, millions of American women exercised their right to vote, declaring for the first time that they, like men, deserve all the rights and responsibilities of citizenship.
By the late 1920s women were entering the workforce in large numbers while men went off to war. Women flocked to the Barbizon in New York City in hopes of being accepted to the prestigious agency, later referred to as the sorority on E. 63rd Street. The Barbizon opened hoping to attract the single, stylish, and thoroughly modern beauties pouring into New York during the Jazz Age to chase their dreams: stardom, independence, a husband. Prospective tenants were required to bring three good references for admission, and were graded on criteria such as looks, dress, and demeanor.

From the beginning, the Barbizon existed as a combined charm school, model agency and dormitory. The building possessed "the greatest concentration of beauty east of Hollywood." The Barbizon, housed many yet-to-be discovered beauties - Joan Crawford, Grace Kelly, Candice Bergen, Sylvia Plath, Ali MacGraw, and many more.In the late 30s early 40s, Conde Nast published many fashion magazines which created a need for photogenic models and ignited the Mad Men period. One of the first being the launch of GLAMOUR magazine in 1939. GLAMOUR Magazine changed the focus from Hollywood starlets to working women. The tagline for the magazine became "the girl with a job".
1961
President John Kennedy establishes the President's Commission on the Status of Women and appoints Eleanor Roosevelt as chairwoman. The report issued by the Commission in 1963 documents substantial discrimination against women in the workplace and makes specific recommendations for improvement, including fair hiring practices, paid maternity leave, and affordable child care.
1963
Congress passes the Equal Pay Act, making it illegal for employers to pay a woman less than what a man would receive for the same job.
1965
Model Composites were invented by Peter Marlowe in London, then printed on paper. The format was changed in 1972 to card format, for filing purposes, and a few other companies started publishing cards for the model industry. Sebastian Sed traded under the name Sed Cards, which are sometimes mis-pronounced as Z ("Zed") or Set cards. Today, the words "models composites" and "comp cards" are generic within the model industry.